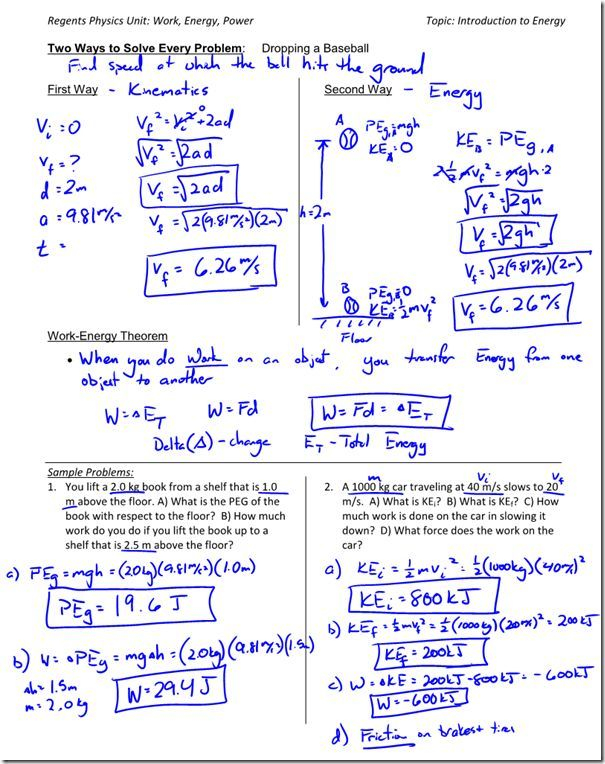
Work Energy Theorem Worksheet - A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was.
Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the.
In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s.
Work Energy Calculations Worksheet Answers Physics Classroom
In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? What is the kinetic energy of.
Worksheet 5 Workenergy Theorem Answer Key
What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s.
SOLUTION Work energy theorem worksheet Studypool
What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work.
SOLUTION Work energy theorem worksheet Studypool
A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of.
Work Energy Theorem Worksheet
(a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? What.
WorkEnergy Theorem Worksheet 1. A ball hangs by a
What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? What force is doing work on the ball as it falls?.
Work Energy Theorem Worksheet Sixteenth Streets
(a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. What is the amount of work.
Solved WORK AND THE WORKENERGY THEOREM Mech HW47 Name 1. A
Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s. What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. The work energy theorem.
This Energy Theorem color by code activity is an engaging
The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. Suppose the total mechanical energy of an object is conserved. (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about the. A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at.
Work And Energy Worksheet Incline
In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was. What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. (a) if the kinetic energy decreases, what must be true about.
(A) If The Kinetic Energy Decreases, What Must Be True About The.
What is the amount of work required to increase a 1100 kg car's speed from 20.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s? What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the thrower’s hand? The work energy theorem states that the change in (a) kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work done on it by the net force. In 1994, leroy burrell of the united states set what was.
Suppose The Total Mechanical Energy Of An Object Is Conserved.
What force is doing work on the ball as it falls? A squirrel (mass 0.9 kg) is running across the road at a speed 4.0 m/s.